The Facts About Psoriasis: Symptoms And Causes
Video Link: https://vimeo.com/182463970
Video Download: The Facts About Psoriasis Symptoms And Causes
Video Stream: The Facts About Psoriasis Symptoms And Causes
The Facts About Psoriasis
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a medical condition that impacts around three percent of people in the United States. There are over five million men and women with psoriasis across the nation. Psoriasis is characterized by inflammation and scaling of the skin and is mainly seen in adult patients, though psoriasis can also become an issue during childhood and adolescence.
There is no gender divide with this condition, as both women and men are equally likely to experience the condition.
How Does Psoriasis Impact Skin Health?
The mechanism which causes scaling and inflammation is that new skin cells, which generally mature beneath the skin and rise to the surface, move to the surface before they have sufficiently developed. It usually takes a newborn skin cell around thirty days to reach the top layer of the skin, but in the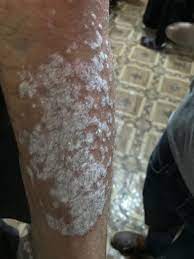 case of Psoriasis, this turnover process can take place in just a matter of days.
case of Psoriasis, this turnover process can take place in just a matter of days.
What Are the Symptoms of Psoriasis?
In the most common form of the condition, Psoriasis leads to high levels of inflammation, and the skin becomes red and topped with scales. The areas where scaling develops are called plaques, which can lead to soreness and severe itching.
Common areas where Psoriasis appears on the body are the soles of the feet, palms, face, lower back, scalp, knees, and elbows, although these patches can appear anywhere on the body.
Other areas where Psoriasis can appear are inside the mouth, on the genitals, and underneath the toenails and fingernails. If Psoriasis occurs on the joints, it can lead the inflamed area to become cracked, and this can lead to bleeding. Psoriasis can also inflame the joints, which leads to arthritis symptoms. If this occurs, it is referred to as Psoriatic Arthritis.
How Can Psoriasis Negatively Impact Quality of Life?
People with Psoriasis can experience life-altering issues resulting from the pain and itching associated with Psoriasis. Also, Psoriasis can sometimes limit movement, leading to limited disability.
Some patients experience severe pain and itching, which prevents them from living and appreciating their day-to-day life, causing sleep to be restless, making bathing a painful chore, and even making walking difficult.
Patients with Psoriasis Plaques on the feet and hands can have issues with any activity involving those body parts, and they may not be able to participate in some sports or even have jobs in some careers. This can even inhibit their ability to care for their loved ones.
Mitigating the symptoms of Psoriasis can require frequent trips to the doctor, and the cost to treat the medical disorder is very high as a result of the chronic nature of the condition.
Psoriasis also impacts self-perception because they are embarrassed about how they look due to their condition. This can make them become withdrawn or make it harder for them to enter romantic relationships. These issues can lead to social isolation, depression, and other psychological issues related to their poor self-image.
What Causes Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a medical condition that results from an overactive immune system and is related to the body's production of T-Cells. T-Cells are powerful immune cells that fight disease and infection.
When a person has Psoriasis, the body activates T-Cells for no reason, and this causes a cascade of immune responses, which causes immature skin cells to rise prematurely while also causing high levels of inflammation.
There is a genetic component to Psoriasis, and scientists have been able to link particular genes to the condition based on their study of particular family lines which are heavily impacted by the condition. Not all patients with Psoriasis have a family history, however.
What Causes Psoriasis Skin Flare-Ups?
Most people with psoriasis experience periods where their skin health becomes more problematic. These periods are known as flares. Psoriasis will temporarily become much worse before recovering somewhat. There are a number of issues that can cause these flares to occur, including weather changes that lead to drier skin, stress, and infection.
Some medications can exacerbate Psoriasis, including lithium and blood pressure medications known as Beta-Blockers. Finally, Psoriasis is more likely to flare up in areas of the skin that have experienced damage or irritation from issues such as infection, sunburn, scratches, and lesions.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Psoriasis
Sometimes, Psoriasis can be problematic to diagnose because it shares symptoms with a number of other skin conditions, such as Sebhoerric Dermatitis. The best way to clinically diagnose Psoriasis is by taking a small patch of the inflamed skin and looking at it through a microscope.
What Are the Types of Psoriasis?
There are a number of kinds of Psoriasis. Below is a partial list:
Plaque Psoriasis - Characterized by inflamed, red skin covered in shiny scales.
Guttate Psoriasis - Characterized by small, round areas of inflamed skin on the scalp, limbs, and trunk. This form of the disease is commonly a reaction to strep throat or other upper respiratory system infections.
Pustular Psoriasis - Characterized by the formation of blisters that are not the result of infection. These blisters are filled with puss and can be caused by stress, infections, medicines, and contact with particular chemicals.
Inverse Psoriasis - Characterized by inflamed areas along skin folds, such as the armpits, beneath the breasts, or around the genitals. Sweating and friction can exacerbate this form of Psoriasis.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis - The rapid and widespread appearance of Psoriasis is commonly caused by corticosteroid medicines or significant sunburn. This form of Psoriasis can also occur as an extension of other Psoriasis forms that are not effectively controlled. This is the most severe form of the condition and requires an immediate visit to a medical professional.
What is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic Arthritis is a medical condition related to and caused by Psoriasis itself. In this case, Psoriasis penetrates into the skin and causes lesions and inflammation of the joints. Patients can experience both forms of Psoriasis simultaneously or either alone at any particular time.
How Can Psoriasis Be Effectively Treated?
There are a number of methods that physicians use to mitigate the symptoms of Psoriasis, dependent upon the specific characteristics of the disease, including the locations of inflammation, the form of psoriasis, the surface area of inflammation, the severity of psoriasis, and the way that the patient has 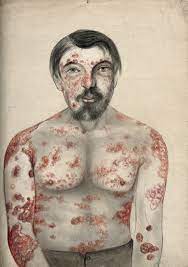 responded to previous treatment.
responded to previous treatment.
The following are some common means by which Psoriasis can be treated:
Injectable and Oral Psoriasis Medication
Phototherapy via Light Exposure
Topical Medications
Like any medication, the treatments listed above can lead to side effects, some minor, some more significant. Always talk to your physician and pharmacist about potential side effects so you can be armed with the knowledge to recognize them.
Some issues make Psoriasis hard to treat. For one, the body can develop a resistance to certain forms of treatment, limiting their effectiveness over time. This is especially true of corticosteroids delivered topically.
Second, every patient responds differently to treatment, and the same medication or therapy may be highly effective for one patient while producing no benefit in a second patient. As a result, physicians often switch therapies until they find one that works effectively with few or no side effects.
- 0001 What Is Adrenal Fatigue [Last Updated On: May 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 23rd, 2020]
- 0002 Understanding Thyroid Function And Diagnosing Thyroid Issues [Last Updated On: May 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 24th, 2020]
- 0003 Twelve Steps To Enhance And Preserve Your Memory [Last Updated On: January 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 25th, 2020]
- 0004 The Psychological And Physiological Effects Of Serotonin [Last Updated On: January 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 26th, 2020]
- 0005 The Facts About Acromegaly [Last Updated On: May 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 28th, 2020]
- 0006 The Effects Of Hgh Deficiency Upon One Of A Pair Of Twins [Last Updated On: January 5th, 2026] [Originally Added On: October 29th, 2020]
- 0007 Resveratrol Anti-aging Supplementation For Longevity [Last Updated On: May 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 30th, 2020]
- 0008 Sermorelin Acetate Injections With Ghrp-6 [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 31st, 2020]
- 0009 Melatonin The Sleep Hormone How It Impacts Your Health [Last Updated On: May 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 1st, 2020]
- 0010 Mark Cuban To Fund Study On Healing Power Of Hgh [Last Updated On: May 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2020]
- 0011 Mark Cuban Advocates For Hgh As A Rehab And Recovery Tool [Last Updated On: January 4th, 2026] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2020]
- 0012 Leptin Hormone Guide: The Effects Of The Satiety Hormone [Last Updated On: January 3rd, 2026] [Originally Added On: November 4th, 2020]
- 0013 Human Growth Hormone Deficiency Impact On Sleeping Habits [Last Updated On: January 2nd, 2026] [Originally Added On: November 5th, 2020]
- 0014 Human Growth Hormone And Liver Regeneration [Last Updated On: January 1st, 2026] [Originally Added On: November 6th, 2020]
- 0015 Hgh Treatment For Fatty Liver Disease On The Horizon [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 7th, 2020]
- 0016 Your Current HGH Level [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 8th, 2020]
- 0017 Ghrelin The Hunger Hormone [Last Updated On: December 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 9th, 2020]
- 0018 Enclomiphene Citrate Andropause Treatment Up For Fda Approval [Last Updated On: December 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 10th, 2020]
- 0019 Dopamine Pleasure Hormone And So Much More [Last Updated On: April 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 11th, 2020]
- 0020 Diabetes Cure On The Horizon [Last Updated On: December 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 12th, 2020]
- 0021 Boost Metabolism To Lose Weight And Maintain Weight Loss [Last Updated On: December 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 13th, 2020]
- 0022 Andropause A Mid-life Hormone Crisis [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 14th, 2020]
- 0023 SOGROYA INJECTIONS FOR HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE DEFICIENCY [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2021]
- 0024 How Do High and Low Estrogen Impact Male Health and Wellness? [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2021]
- 0025 The Effects Of Hormone Imbalance On Belly Fat [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2021]
- 0026 Could Sunlight Help Remove Rogue Hormones from the Water Supply? [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 29th, 2021]
- 0027 Weekly HGH Therapy Just as Effective as Daily Injections [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 18th, 2021]
- 0028 DHEA and Testosterone: A winning team! [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 19th, 2022]
- 0029 Animal Research Discovers Link Between Exercise, HGH, and Cognitive Ability [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 20th, 2022]
- 0030 Weekly Hormone Treatments for Adult HGH Deficiency with Sogroya [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 14th, 2022]
- 0031 Ancient Critters Made Human Hormone System What It Is Today [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 26th, 2022]
- 0032 How Substance Abuse Can Affect Your Hormone Levels [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 4th, 2022]
- 0033 A Holistic Approach to Health and Water Safety [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 7th, 2025]
- 0034 Understanding the Role of Sogroya in Adult Human Growth Hormone (HGH) Deficiency Treatment [Last Updated On: February 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 11th, 2025]
- 0035 Andropause: An Examination of Mid-life Hormonal Shifts in Males [Last Updated On: February 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 13th, 2025]
- 0036 Sermorelin Acetate Therapy: A Comprehensive Insight into its Benefits with GHRP-6 [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2025]
- 0037 The Dynamic Duo of Male Vitality: Testosterone and DHEA [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2025]
Word Count: 1203






