A Brief Guide To Endocrinology
Video Link: https://vimeo.com/499047484
Video Download: A Brief Guide To Endocrinology
Video Stream: A Brief Guide To Endocrinology
Endocrinology is an area of medical science that is devoted to the study of Hormones. The Endocrine System represents the variety of organs and glands which are responsible for hormone production and regulation.
Endocrinologists are heavily involved in investigating medical disorders and conditions that impact human health via Hormone Imbalance, including 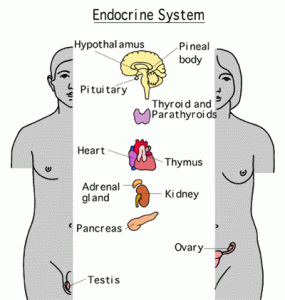 infertility, Low-T, HGH Deficiency, Thyroid Insufficiency, Obesity, Hypertension, and more.
infertility, Low-T, HGH Deficiency, Thyroid Insufficiency, Obesity, Hypertension, and more.
The Endocrine System is incredibly complex, but some of the central glands in the system are the Ovaries, Testes, Pancreas, Adrenals, Parathyroids, Thyroid, Pituitary, Pineal, and Hypothalamus.
What Do Hormones Do?
Every Hormone in the body has at least one job to do. In the case of many hormones, such as HGH and Serotonin, they perform various functions depending on physiological circumstances.
Hormones are often called Chemical Messengers because they help communicate with different body parts. The end-point where a Hormone completes its task is known as the Target and can be located pretty much anywhere in the body. It's estimated that as many as forty hormones can simultaneously be active in the bloodstream.
The following is a brief list of functions modulated by Hormones:
- Mood
- Reproduction
- Sexual Function
- Metabolism
- Growth and Physical Development
- Blood Sugar Regulation
The Perils of Hormone Imbalance
Our hormones interact in a very complex way. Proper function depends on Hormone Cascades, which are delicately balanced. If one hormone isn't being produced correctly, it affects entire systems.
The human body is excellent at maintaining Hormone Balance on its own, but sometimes things can get out of whack in a way that requires outside intervention. Endocrinologists are doctors that specialize in the area of Hormone Health.
Parts of The Endocrine System
Adrenal Glands
The Adrenals are critical to regulating blood pressure and salt/water balance. These glands are situated just above the kidneys. They also play a pivotal role in metabolism and stress response. While they produce sex hormones throughout the lifespan, they also trigger the sex organs' development. The three main classes of hormones that the adrenal glands produce are androgens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids.
Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus is considered the prime control center of the brain. It links the nervous system and the endocrine system via the Pituitary. The Hypothalamus produces many precursor hormones and controls involuntary duties such as thirst, hunger, and temperature regulation.
Pituitary Gland
The Pituitary is tiny, about the size of a single pea, but it has enormous responsibilities. The Pituitary releases hormones that act upon other glands such as the reproductive organs, the adrenals, and the thyroid. It's often called the Master Gland for this reason. Growth, sexual, and renal function are all high priorities for the Pituitary.
Pineal Gland
The Pineal gland is critical to the circadian rhythm. It's deep in the brain's core and is responsible for the production of melatonin, which controls our sleeping habits.
Pancreas
The Pancreas does double duty as a link between the digestive and endocrine systems. The Islets of Langerhans are the parts of the Pancreas responsible for hormone production. The Pancreas helps control metabolism and blood sugar, and pancreatic malfunction is the prime cause of Diabetes.
Parathyroid Glands
The human body has four Parathyroid glands, all around the size of a pencil tip. They are located behind the thyroid, deep in the neck. The glands are responsible for controlling calcium levels, not only in the bones but throughout the body. The glands produce Parathyroid Hormone to modulate calcium 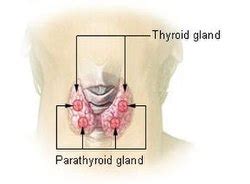 and interact with the intestines to draw calcium from the digestive tract.
and interact with the intestines to draw calcium from the digestive tract.
Thyroid gland
The thyroid is also located in the neck and is responsible for converting Iodine into T3 and T4. These hormones are critical to heart rate, temperature, and blood pressure. They also modify how the body responds to the influence of other hormones. The thyroid also down-regulates calcium.
Testes
Testes are the male glands. The Testes produce Testosterone and other sex hormones, which control sexual development and support sexual health. Testosterone also has unique effects on several different systems.
Ovaries
As opposed to the testes, women have Ovaries as their primary sexual glands. The ovaries are responsible for spurring sexual development. The ovaries produce progesterone and estrogen, which are vital to menstrual regulation and pregnancy.
- 0001 Six Questions You Should Ask Yourself Before Your Trip To The Doctor [Last Updated On: May 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 16th, 2020]
- 0002 Requirements For Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: January 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 17th, 2020]
- 0003 Hgh Testimonials And Reviews [Last Updated On: January 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 18th, 2020]
- 0004 Clomiphene Citrate Information And Guide [Last Updated On: May 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2020]
- 0005 Breast Cancer: Separating Fact From Fiction [Last Updated On: January 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2020]
- 0006 Managing Cardiovascular Risks Associated With Prostate And Breast Cancer [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 5th, 2021]
- 0007 Presence of Specific Genetic Allele Influences Response to Growth Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 15th, 2021]
- 0008 Macimorelin A New Diagnostic Tool for Diagnosing Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 22nd, 2021]
- 0009 Ipamorelin Acetate with CJC 1295 for HGH Deficiency [Last Updated On: February 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 29th, 2022]
- 0010 Why Do My Friends Feel So Good While I Feel So Bad? [Last Updated On: March 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 20th, 2022]
- 0011 My Vacations Weren’t Vacations Anymore [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 28th, 2022]
- 0012 Racing Ferraris – A Stressful Way to Earn a Living [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2022]
- 0013 Symptoms of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Adults [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: September 15th, 2022]
- 0014 HGH and Intellectual Improvements [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2023]
- 0015 Abie’s Lies [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2023]
- 0016 Revolutionizing the Silver Years: Age-management Warriors Defying Time’s Grip [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2025]
- 0017 Introduction: A Personal Story [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
Word Count: 705






