Vitamin D The Sunlight Vitamin
What is Vitamin D, and Why is It Important?
Vitamins are nutrients the body needs that it can't make on its own. Vitamin D3 is unique because the body can produce the nutrient naturally, but most people still don't get enough of it.
The human body can produce its own Vitamin D using two primary ingredients: Cholesterol and Sunlight. Vitamin D is a steroid hormone in the same 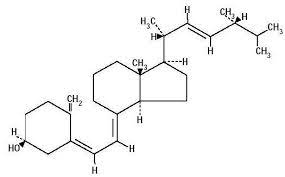 category as other hormones such as Testosterone, Cortisol, and Estrogen.
category as other hormones such as Testosterone, Cortisol, and Estrogen.
Vitamin D is important because it protects the body from a number of medical conditions, and it also has a substantial impact on our genetic expression. Vitamin D is critical for the body to function correctly, encouraging optimal health and wellness.
Vitamin D Deficiency Common Throughout the World
Scientists have understood the importance of Vitamin D for decades. Still, new research continues to unearth new benefits, showing that the nutrient is vitally essential for preventing premature aging and softening the effects of the aging process itself.
Even though our body does have the capacity to create its own Vitamin D, there are millions upon millions across the world that experience adverse effects directly as a result of Vitamin D Deficiency.
This isn't just a 3rd world problem either; Vitamin D Deficiency is a significant problem in America and worldwide. Medical research has shown that if everyone on earth got the Vitamin D, they needed throughout their lives, the risk of various cancers would drop by 50%!
How Does Sunlight Produce Vitamin D?
Like most mammals, humans can produce their own Vitamin D3 if they expose themselves to sufficient sunlight. This is an effective way for most people to get sufficient Vitamin D, at least until around the fifties.
The problem with this method is that too much exposure to ultraviolet light can lead to an increased incidence of skin cancer and prematurely ages the skin. Because of these two reasons, most medical professionals and nutritionists advise against getting Vitamin D primarily through sunlight and recommend Vitamin D supplements as a safer and healthier alternative.
When was Vitamin D Discovered?
The scientific name for Vitamin D3 is Cholecalciferol, which is undeniably essential for optimal health. Like most complex nutrients, Vitamin D was not discovered until over one hundred years ago, when physicians attempted to discover a proper medical treatment for rickets. This dangerous bone disease commonly affects pediatric patients.
Vitamin D and Rickets
The disease reached epidemic levels in the 19th century, at the heart of the Industrial Revolution. During this period, agricultural economies across the western world quickly converted from farming to factory work, and everyone, even children, began working in dark factories, away from sunlight.
These factories were poorly lit and dirty, and significant industrial cities quickly became highly polluted, diminishing the influence of sunshine, even outdoors.
 Medical scientists discovered that men, women, and children who lived and worked in the sunshine were at significantly less risk of rickets than those who lived in industrial or cloudy cities further north. Using this demographic evidence, doctors could deduce that a lack of sunlight caused rickets.
Medical scientists discovered that men, women, and children who lived and worked in the sunshine were at significantly less risk of rickets than those who lived in industrial or cloudy cities further north. Using this demographic evidence, doctors could deduce that a lack of sunlight caused rickets.
They also found that a prescription of cod liver oil could safeguard the patient entirely from the disease. Via this cure, physicians proved that Vitamin D deficiency was a condition of deficiency rather than a disease caused by a bacterium or virus. Although it would be years before researchers discovered Vitamin D, effective treatment via supplementation was already discovered.
How Common is Vitamin D Deficiency?
Even today, Vitamin D deficiency is still widespread. A French study demonstrated that fourteen percent of adults had deficient Vitamin D levels. In another research, it was discovered that more than forty percent of physicians that did not take Vitamin D supplements had clinically low levels of Vitamin D by the last days of winter.
Physicians that did supplement their natural Vitamin D production over the course of the winter only experienced Vitamin D Deficiency at a rate of around ten percent.
Vitamin D Deficiency Easily Prevented
Based on the history of Vitamin D, it is crystal clear that Vitamin D Deficiency is a significant medical condition. Even though this condition is highly preventable, millions across America don't get the necessary Vitamin D.
Rickets may be the most apparent symptom of Vitamin D Deficiency. Still, there are many other issues related to the condition. As mentioned earlier, Vitamin D Deficiency can cause the body to age more quickly.
The vitamin also has significant anti-inflammatory benefits; the nutrient also impacts psychological health and can reduce the effects of depression. There is even strong evidence that Vitamin D can enhance the human lifespan and even increase the longevity of the neurons in the nervous system and the brain.
Vitamin D Benefits
The following is just a short list of the benefits of Vitamin D3:
Osteoporosis is one of the most life-changing issues aging women face, which significantly increases frailty and the danger of experiencing bone fractures and breaks. The most dangerous of these breaks is hip fracture, which severely increases mortality among aging patients. One piece of research financed by the Women's Health Initiative discovered that older female patients taking calcium carbonate and Vitamin D3 supplements experienced twelve percent fewer hip fractures than patients in the control group. The dose which produced these benefits was 800 IU daily.
Vitamin D3 is an integral nutrient that protects the immune system's health and helps the body ward off a wide variety of diseases. Each of the active cells of your immune system has receptors for Vitamin D, and there is clear evidence that Vitamin D deficiency impairs the body's resistance to infection and boosts the chances of symptoms of a number of autoimmune disorders.
In particular, Vitamin D protects the respiratory system from viral infection. Patients with Vitamin D Deficiency are more likely to come down with the flu and are also more likely to become a victim of tuberculosis. Deficiency also impacts the severity of both diseases.
A recent study presented at the American College of Cardiology in 2010 provided robust evidence that patients with Vitamin D Deficiency were more likely to experience cardiovascular disease. An effective Vitamin D3 supplement was sufficient to reduce the risk of death via cardiovascular disease by
 thirty percent!
thirty percent!
A growing body of evidence suggests that Vitamin D can prevent cancer cells from proliferating. Although excessive exposure to sunlight indeed increases the chances of experiencing skin cancer, many types of cancer are mitigated by sunlight therapy which enhances Vitamin D synthesis. Among the types of cancer that sunlight therapy proves beneficial include cancers of the kidneys, pancreas, and small intestine, as well as myeloma and Hodgkin's lymphoma. Vitamin D Supplementation and sun exposure are also valid aspects of the treatment of prostate, rectal, stomach, uterine, bladder, colon, and cancer of the vulva.
Vitamin D Supplementation also reduces the risk of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease, although the connection is not yet fully understood. In one survey, fifty-five percent of patients with Parkinson's Disease experienced Vitamin D Deficiency, and over forty percent of Alzheimer's patients experienced a similar deficiency.
Vitamin D supplements also prove beneficial for patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Patients treated with Vitamin D were more able to walk and engage in daily activities. They also had fewer lesions. Patients with Vitamin D Deficiency are also more likely to experience Multiple Sclerosis relapses. Demographic evidence shows that people living closer to the equator are less likely to experience Multiple Sclerosis, which also suggests a strong connection between Vitamin D and the condition itself.
Simultaneous Calcium and Vitamin D3 supplementation have been clinically shown to reduce general mortality risk in elderly patients by around nine percent.
How to Get Enough Vitamin D
The most obvious way to ensure you get sufficient Vitamin D is to get a reasonable amount of sunlight each day. It's essential to be cautious when utilizing this natural method, however. Spend no more than fifteen minutes in unscreened, direct sunlight. More has been shown to increase the risk of experiencing skin cancer.
We recommend getting in direct sunlight for around 5-10 minutes per week. You don't have to walk around with your shirt off, however. Sunlight exposure to your face, hands, and arms should be sufficient to provide optimal Vitamin D Synthesis.
Vitamin D Boosting Foods
You can also increase your body's capacity for Vitamin D if you consume particular foods. Fatty fish are some of the best options, including sardines, mackerel, salmon, tuna, catfish, and eel. If you don't eat meat, some of the best sources include egg yolks and fortified foods such as milk, cheese, and cereal.
cereal.
How Much Vitamin D Do I Need?
Different groups have different recommendations for optimal Vitamin D supplementation. The International Osteoporosis Foundation suggests 800-1000 IU of Vitamin D daily. The U.S. Institute of Medicine suggests 600 IU of Vitamin D for individuals up to seventy years of age and 800 IU for older men and women.
It's in your best interest to take the maximum daily recommendation you find from a respected source because Vitamin D has very low toxicity. Taking 10,000 IU daily for three months, or 300,000 IU in a single day, is considered dangerous, far above any recommended dose.
When taking any supplement, it's essential to understand that too much of even the most beneficial medication can harm your health.
Vitamin D: An Easy Way to Safeguard Your Health and Enhance Longevity!
Unlike pharmaceuticals, Vitamin D is a natural nutrient. It's vital to your health, and you can make it on your own in the presence of sunlight. We need the vitamin all throughout our lives, and our need for supplementation grows as our body becomes less efficient at naturally producing the nutrient.
Luckily, it's cheap and easy to get all the Vitamin D you need to maximize your vitality and minimize the associated health risks!
References
Aranow, C. "Vitamin D and the immune system." Journal of Investigative Medicine. 2011 Aug;59(6):881-6
Evatt, M.L., et al. "Prevalence of Vitamin D Insufficiency in Patients With Parkinson Disease and Alzheimer Disease." Archives of Neurology 2008; 65(10):1348-1352
Holick, M.F. "Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases, cancers, and cardiovascular disease." American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2004 December; 80(6 Supplement):1678S-88S
Jackson RD, et al. "Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation and the risk of fractures." New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;354:669-83
Mohr, S.B. "A brief history of vitamin D and cancer prevention." Annals Epidemio. 2009 Feb; 19(2):79-83.
Regulska M, et al. "Involvement of PI3-K in neuroprotective effects of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 analog - PRI-2191." Pharmacology Reports. 2006 Nov; 58:6,900-907
Rejnmark, L., et al. "Vitamin D with Calcium Reduces Mortality: Patient Level Pooled Analysis of 70,528 Patients from Eight Major Vitamin D Trials." Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2012 May 17
Schleithoff S.S., et al. "Vitamin D supplementation improves cytokine profiles in patients with congestive heart failure: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial." American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2006 Apr; 83:4, 754-759
Tangpricha V, Pearce EN, et al. "Vitamin D insufficiency among free-living healthy young adults." American Journal of Medicine 2002; 112:659-62
Vitamin D Council, "Am I getting too much Vitamin D?", http://www.vitamindcouncil.org/about-vitamin-d/am-i-getting-too-much-vitamin-d/, retrieved 22 March 2014
- 0001 Vitamin B3 Niacin The Vitamin You Really Feel [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 24th, 2022]
- 0002 The Immediate, Tangible Effects of Vitamin B3 Niacin [Last Updated On: February 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 15th, 2025]
Word Count: 1857






