Hormone Replacement Therapy Blood Testing
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Test your HGH Blood Levels
HGH and Testosterone Hormone Replacement Therapy Testing
As we've mentioned elsewhere, one of the most critical steps of our Hormone Replacement Therapy diagnostic process is the blood testing we conduct on the sample you provide during your physical.
After our affiliate physician draws your blood sample, he or she will seal the sample and send it securely to the diagnostic testing firm LabCorp. You may also choose to go through your physical on-site with a representative from LabCorp, where your blood sample can be stored and analyzed on-site.
LabCorp will process your blood sample over the course of a few days, and your results will be available within a week of providing your sample.
The results of your blood test will look very complicated on paper. Still, your medical representative at the Conscious Evolution Institute will go over the details with you and simply explain them. Every one of these tests will increase the ability of your prescribing physician to make an accurate diagnosis.
Hormone Blood Panel Tests
Plasma Homocystine Test
Homocysteine is an amino acid that our body manufactures from foods, especially meat. Although our bodies need a certain amount of Homocysteine for proper function, elevated Homocysteine levels correlate with various health conditions.
High Homocysteine Levels increase the risk of blood clot formation, stroke, hardened arteries, embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and heart attack. It may also increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Patients with abnormally high levels of Homocysteine in their bloodstream may need to be tested for heart health before being approved for Hormone Replacement Therapy with Testosterone and Human Growth Hormone.
Lipid Panel with LDL/HDL Ratio
The Lipid Panel is a small group of tests used to measure the level of cholesterol present in your bloodstream. These tests will uncover your LDL Cholesterol, which is also referred to as Bad Cholesterol. The ideal LDL Cholesterol Level for healthy individuals is between 100-129 mg/dL.
For patients at risk for heart disease, an LDL Cholesterol level of 100 mg/dL or less is best for the body. When LDL Cholesterol Levels are too high, this increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems significantly.
HDL cholesterol is also referred to as Good Cholesterol. For this form of cholesterol, the higher your level, the better.
For men, an HDL Cholesterol Level of 40-49 mg/dL is considered normal, and 50-59 mg/dL is considered ideal for women.
A level of 60 mg/dL is optimal for both sexes. HDL Cholesterol has a restorative and protective effect on cardiovascular health and is associated with reduced risk for heart attack, cardiovascular disease, and stroke.
Triglycerides, like LDL Cholesterol, are necessary for normal, healthy heart function, but elevated levels harm your health. Triglycerides in the bloodstream are directly correlated with your diet and fitness level, and triglycerides can be controlled by exercising and eating a healthy diet. Healthy Triglyceride levels are considered below 150 mg/dL.
Your Lipid profile will also gauge the total cholesterol level in your bloodstream. Using these other tests, we will also be able to determine the HDL/LDL Cholesterol ratio in your bloodstream. The higher this ratio is, the better it is for your heart health.
Levels of Very Low-Density Lipoprotein can also be determined. These Lipoproteins are responsible for transporting various cholesterol throughout the body.
Testosterone Free and Total
As you can easily imagine, the levels of Free Testosterone and Total Testosterone in your bloodstream directly correlate with the amount of Testosterone available to your body. Total Testosterone refers to all of the Testosterone present in your blood sample, in all forms.
Free Testosterone refers to Testosterone in your bloodstream, which is unbound. Free Testosterone is Testosterone that isn't being used by your body.
If you have too much Free Testosterone, your body isn't using the Testosterone that your Testes and Adrenal Glands are producing effectively. If Total Testosterone production is too low, your glands are not producing Testosterone effectively, which can occur for various reasons, most of which can be deduced by other tests in this hormone panel.
Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Testing
This is the single, most crucial test about your Human Growth Hormone Function. It may be counter-intuitive, but directly testing HGH Production is not an effective way to assess your need for HGH. When the pituitary gland secretes HGH, or when it is injected into the body, it only remains in the bloodstream for a short period of time.
It quickly disperses throughout the body to areas where it is metabolized. Most HGH circulates through the liver, converting it into a hormone known as Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1. IGF-1 performs most of the tasks associated with Human Growth Hormone, and this hormone remains active in the body for a few days, making it a more effective means to monitor HGH Secretion by proxy.
If IGF-1 Levels are low, this is robust evidence that you are suffering from HGH Deficiency.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone Testing
These tests are critically important for the accurate diagnosis of Testosterone Deficiency. In males, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone, also known as FSH, is responsible for the healthy production of sperm. In males, Luteinizing Hormone (or LH) is responsible for the proper production of Testosterone. FSH and LH production is mediated by both the Pituitary Gland and the Hypothalamus.
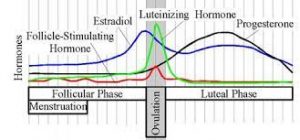 The levels of these two hormones will help indicate the source of your Testosterone Deficiency. For most adult males, Low-T results from reduced signaling from the hypothalamus, which directly leads to reduced stimulation of the Testes. In most men, the Testes are perfectly capable of producing Testosterone; they simply don't receive the signal to do so.
The levels of these two hormones will help indicate the source of your Testosterone Deficiency. For most adult males, Low-T results from reduced signaling from the hypothalamus, which directly leads to reduced stimulation of the Testes. In most men, the Testes are perfectly capable of producing Testosterone; they simply don't receive the signal to do so.
If LH and FSH Levels remain normal or high, this means that the deficiency is the result of the testes. Suppose the levels of these hormones are abnormally low. In that case, this shows that the deficiency results from age-related Andropause or some other sudden complication that inhibits the hypothalamus or the pituitary.
Estradiol Testing
Estradiol is a member of the Estrogen family, but it still plays an essential role in male health. Balanced Estradiol Levels contribute to healthy body fat percentage and strong bones. Estradiol Testing is another way your doctor can assess your need for Testosterone Hormone Replacement Therapy.
If your Estradiol Levels are abnormally low, this provides evidence that you may suffer from Low-T. Estradiol is naturally made by the male body primarily through the breakdown of Testosterone. If there is insufficient Testosterone in the bloodstream, the body will often have abnormally low levels of Estradiol. One of the most damaging symptoms of Estradiol Deficiency is osteoporosis.
High Levels of Estradiol may indicate that Testosterone HRT is not suitable for you because this is a sign that you may be at elevated risk of Prostate Cancer or cardiovascular complications.
Complete Blood Count With Differential/Platelet
This widespread blood test is frequently performed during many general-health check-ups. The CBC Test is a panel of blood tests that measure the levels of various cells in your bloodstream. The cell concentrations tested are platelets, white blood cells, hemoglobin, red blood cells, and hematocrit.
Each aspect of testing measures a different aspect of the health of the body. A number of other tests can also be included in this Hormone Panel, but these are the most common:
Red Blood Cell Count - Tests for Anemia and other disorders.
White Blood Cell Count - Tests the health of the immune system.
Platelet Test - This measures the ability of your bloodstream to form and clear blood clots.
Hemoglobin Test - Measures your body's capacity to deliver oxygen to the body
Hematocrit Test - Hematocrit concentration is related to numerous different disorders, including leukemia and anemia.
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel
Like the Complete Blood Count, the Comprehensive Metabolic Panel is a group of tests that measure various aspects of human health. The CMP is a collection of fourteen tests that measure the functional capacity of various different organs of the body.
The CMP is a general test often performed during routine physicals. The various tests performed in this panel measure the presence of a number of essential hormones released by the liver and the kidneys, and there are also tests that measure fluid and electrolyte balance.
These tests are used to find evidence for various medical conditions such as hypertension and diabetes. These tests can also discover underlying issues with parathyroid function.
with parathyroid function.
PSA Testing
PSA Testing is one of the most critical tests before initiating Low-T Treatment or HGH Hormone Replacement Therapy. PSA is short for Prostate-Specific Antigen. There is nothing inherently dangerous about elevated PSA Levels, but High PSA Counts are a recognized, common symptom of Prostate Cancer.
If your blood test comes back indicating that your PSA Levels are high, and you have never engaged in Hormone Replacement Therapy in the past, you need to undergo further testing for Prostate Cancer. If you have Prostate Cancer, HGH and Testosterone HRT may exacerbate existing cancer and are not recommended until further study is conducted.
Testosterone Hormone Replacement Therapy also has the side effect of increasing PSA Levels, but this increase is not correlated with an elevated risk of Prostate Cancer. Both Testosterone HRT and Prostate Cancer elevate PSA Production.
The earlier hypothesis that PSA Levels correlated directly with Prostate Cancer Risk led many to believe that Testosterone Replacement could enhance the risk of this form of cancer, but all subsequent research has revealed that this is a benign side-effect.
Cortisol Testing
Cortisol Testing is an essential aspect of diagnosing both Testosterone and HGH Deficiency. Cortisol is a stress hormone produced by the human body which controls pain tolerance, fight-or-flight response, and energy management, among other things.
Cortisol at normal levels is necessary and healthy for the body's normal function, but excess levels of Cortisol hurt your overall Hormone Balance. Cortisol is a member of the Glucocorticoid family and is derived from the same hormones used to manufacture Testosterone in the human body. High cortisol levels also inhibit HGH Production.
Cortisol Testing is also used to diagnose a disorder known as Cushing's Syndrome, a metabolic disorder in which the body produces excessively high levels of Cortisol to the detriment of human health. One of the most significant symptoms of Cushing's Syndrome is extreme fatigue.
Dependent upon the severity of High Cortisol Levels, this test can either provide evidence that Hormone Replacement Therapy is needed or that Cushing's Syndrome is the primary cause of your deficiency.
DHEA-Sulfate Testing
This test is performed to evaluate the healthy function of the Adrenal Gland. DHEA stands for dehydroepiandrosterone. This hormone is a part of the Androgen family and is released by the Adrenal Gland in combination with other male hormones. DHEA-Sulfate is the form of DHEA which circulates freely through the bloodstream.
Individuals that suffer from DHEA Deficiency generally also suffer from Testosterone Deficiency. Still, DHEA Deficiency implies that the medical source of the problem is the result of a malfunction of the Adrenal Gland or a result of a processing malfunction in the brain. Testosterone Replacement Therapy can be successful under these circumstances but may need to be combined with other forms of treatment.
Thyroid Hormone Panel
The goal of this series of blood tests is to measure the functional capacity of your thyroid gland. The Thyroid Hormone Panel will always include Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Testing. It may also necessitate tests of Total Thyroxine (T4), Free Thyroxine (T4), and Free Tri-iodothyronine (T3) that your body is producing.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone is a precursor hormone that encourages the Thyroid to release T3 and T4. Total T4 Testing measures the amount of T4 released by the Thyroid Gland. Free T4 Testing measures the amount of T4 delivered to cells. T3 Testing measures the amount of active Thyroid Hormone which can be utilized by the body's cells.
This test ensures that your Thyroid is functioning correctly because two of the most common symptoms of Thyroid Deficiency are weight gain and exhaustion, two common symptoms of both HGH Deficiency and Low-T.
Insulin Fasting Blood Test
Insulin is a hormone vital to human function. Insulin is a hormone released by the pancreas that helps take carbohydrates you digest and ship them to cells throughout your body. In some men and women, the body becomes resistant to Insulin over time, leading to a condition known as Type-Two Diabetes.
Diabetes is a severe medical disorder that shares some symptoms in common with HGH and Testosterone Deficiency. Type-2 Diabetes can lead to severe fatigue because insulin resistance prevents the body from receiving energy optimally.
If your Insulin Levels are too high, then this means that you may be either Diabetic or Pre-Diabetic. In this case, you need to make changes in your life that encourage healthier Insulin Balance. You may still qualify for some forms of Hormone Replacement Therapy, but it is essential to get your Insulin Levels under control.
Hemoglobin A1C Test
Hemoglobin A1C Testing is another diagnostic test used to discover underlying signs of Diabetes, which may mimic signs of Hypopituitarism or Hypogonadism. If you have ever seen advertisements for Blood Sugar Monitors on television, these products are designed to measure Hemoglobin Levels in the bloodstream.
Hemoglobin is the biological form that glucose takes in the bloodstream after processing. In patients that are Diabetic or Pre-Diabetic, Hemoglobin Levels are elevated in the blood, meaning that the patient is suffering from High Blood Sugar because their body is not appropriately shipping glucose around the body.
As with Insulin Testing, if Hemoglobin Concentration in the blood is too high, this is a sign of Diabetes, and you need to get your Blood Sugar under control through lifestyle changes or treatment. You may still qualify for some forms of Hormone Replacement Therapy after your health status has been appropriately evaluated and treated.
Serum Ferritin Test
This test is essential for accurately diagnosing Testosterone and Human Growth Hormone Deficiency because it rules out alternate forms of fatigue and low energy levels associated with both of these forms of Hormone Deficiency.
Ferritin is a protein used by the body to transport iron throughout the bloodstream so that various organs can effectively use it. Ferritin is also typically found in the bone marrow, skeletal muscles, spleen, and liver.
found in the bone marrow, skeletal muscles, spleen, and liver.
The human body produces Ferritin in response to iron present in the blood. The greater iron levels in the blood, the more Ferritin will be present.
Abnormally low Ferritin Levels are a sign of anemia, a medical condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough usable iron in the diet. If low levels of Ferritin are found in the bloodstream during Hormone Testing, this may rule out your need for Hormone Replacement Therapy.
Sex-Hormone Binding Globulin Test
This test aims to discover the concentration of SHBG in your bloodstream. Sex-Hormone Binding Globulin, also known as Sex-Steroid Binding Globulin, is responsible for transporting the sex hormones of the body throughout the bloodstream.
Sex hormones are divided into two classes, Androgens, and Estrogens. This test is essential for diagnosing Testosterone Deficiency because Testosterone is a member of the Androgen family. If SHBG levels are abnormally low, this can cause the body to distribute Testosterone abnormally throughout the body, inhibiting the beneficial effects of Testosterone.
SHBG can also indirectly measure Testosterone Levels by comparing the ratio of Free Testosterone bonded to SHBG to unbonded SHBG molecules.
- 0001 What Is Male Hypogonadism? [Last Updated On: October 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 18th, 2020]
- 0002 What Is Low-t And How Can It Effect My Life? [Last Updated On: August 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 22nd, 2020]
- 0003 Identification Of Late Onset Hypogonadism In Middle Aged And Elderly Men [Last Updated On: September 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 24th, 2020]
- 0004 Importance Of Hormone Balance For A Man's Health [Last Updated On: August 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 25th, 2020]
- 0005 Subcutaneous Injection Procedures [Last Updated On: August 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 30th, 2020]
- 0006 Genetics And Gene Therapy. What Are Genes? [Last Updated On: June 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 2nd, 2020]
- 0007 Whey Protein [Last Updated On: June 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 3rd, 2020]
- 0008 Gh-rh [Last Updated On: June 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 12th, 2020]
- 0009 How Does Growth Hormone Testing Work? [Last Updated On: February 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 15th, 2020]
- 0010 Important Figures In Hormone Replacement Therapy Research [Last Updated On: May 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 16th, 2020]
- 0011 Certified Age-management And Longevity Professionals [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 28th, 2020]
- 0012 Bio-identical Genotropin Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: May 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: September 4th, 2020]
- 0013 HGH Injections [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2023] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2021]
- 0014 Growth Hormone Injection Treatment For Women [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2021]
- 0015 Buy Growth Hormone Injection Treatment For Men [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2021]
- 0016 The Conscious Evolution Institute For Quality Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: September 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 10th, 2021]
- 0017 25 Foods That Can Improve Your Health [Last Updated On: September 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2021]
- 0018 Change Your Life With A Conscious Evolution Lifestyle [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2021]
- 0019 Understanding The Various Causes Of Human Obesity [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2021]
- 0020 Male Hormone Replacement Therapy Blood Panel [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2021]
- 0021 Getting Started With Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2021]
- 0022 Buy Female Blood Diagnostics [Last Updated On: September 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2021]
- 0023 Low Testosterone and other Sex Drive Killers that Cause Low Libido in Men [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 1st, 2022]
- 0024 The effects of Human Growth Hormone (HGH) on the skin [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2022]
- 0025 Testicle Tanning – See Through the Hype [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 30th, 2022]
- 0026 Lean Muscle Mass Critically Important to Healthy Aging [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: June 28th, 2022]
- 0027 Can Vitamin B6 Help Relieve Anxiety? [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 2nd, 2022]
- 0028 A Chemical Found in Common Household Items May Disrupt a Hormone Necessary for Healthy Pregnancy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 2nd, 2022]
- 0029 Matching Libidos Ensure Healthy Relationships [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 11th, 2022]
- 0030 How Fluctuating Libidos Affect Aging Men and Women [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 10th, 2023]
- 0031 Adopting a Conscious Evolution Lifestyle for Improved Health and Longevity [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 9th, 2025]
- 0032 Male Hormone Replacement Therapy: Diagnostic Blood Test Regime [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 13th, 2025]
- 0033 Unleash the Power of Vitamin B6: The Natural Antidote to Anxiety! [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2025]
- 0034 The Impact of Human Growth Hormone Deficiency in Men [Last Updated On: February 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 15th, 2025]
- 0035 Maintaining Lean Muscle Mass: A Crucial Facet of Healthy Aging [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 15th, 2025]
- 0036 Introduction to Testicle Tanning [Last Updated On: February 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 16th, 2025]
- 0037 Introduction to Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 17th, 2025]
- 0038 Importance of Matching Libidos for Healthy Relationships [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 19th, 2025]
Word Count: 2562






